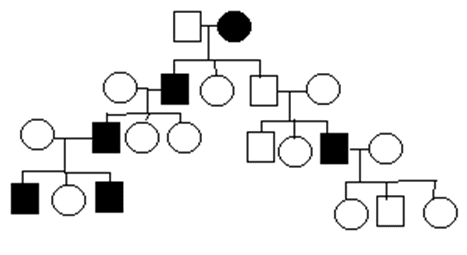
1- Which of the following mutation types is expected to produce the mildest form of disease?
2- Individuals who inherit two active copies of the insulin-like growth factor 2 gene (Igf2)- - one from their mother and one from their father--are at increased risk for developing the Wiedemann-Beckwith syndrome (large size at birth, large tongue, increased incidence of kidney tumors). This situation is an example of?
3- Which of the following features would you be least likely to observe in neurofibromatosis type 1?
4- Concerning retinoblastoma, which of the following is not predicted by the two-hit model?
5- Which of the following will yield the highest recurrence risk for Down syndrome in a family?
6- In which of the following chromosome disorders is the extra chromosome contributed in nearly equal proportions by the mother and the father?
7- A crossover event that places the SRY gene on the X chromosome can cause?
8- Which of the following is not often seen in the child with Down syndrome?
9- What is the best explanation for the muscle weakness seen in 8-10% of females who are heterozygotes for the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene?
10- has been suggested that schizophrenia is more severe and has an earlier age of onset in the more recent generations of schizophrenia families. If so this would be an example of?
11- Which of the following is true of chromosome abnormalities?
1- Your class of 100 people has been typed for a two-allele polymorphism (alleles labeled 1 and 2), and the following 3 genotype counts were obtained: 1,1/30 1,2/50 2,2/20
|
1,1 |
30 |
|
1,2 |
50 |
|
2,2 |
20 |
What are the gene frequencies for alleles 1 and 2 in you class?.
2- Suppose that the prevalence of hemophilia A (x-linked recessive) among the females of a population is 1/1,000,000. Based on this figure, what is the gene frequency in this population, and what would the prevalence be among males?.
3- Continuing question 2, suppose now that half of the females who have hemophilia A are manifesting heterozygotes. Will this raise or lower the gene frequency estimate? Why?.
4- A woman comes to your office for genetic counseling because her niece has cystic fibrosis (autosomal recessive). She is concerned that she might be a CF carrier. What is the probability that this woman is a heterozygous carrier for a cystic fibrosis mutation?.
5- A man and woman are both affected by an autosomal dominant disorder that is lethal in the embryonic period in homozygotes. The disease has 50% penetrance in heterozygotes. On average, what proportion of their live-born offspring will be affected?.
6- A woman who is a known heterozygous carrier of a PKU mutation marries her half second cousin (see pedigree). What is the probability that this couple will produce a child with PKU (autosomal recessive disorder)?.
7- A color-blind (X-linked) male with hemophilia A mates with a normal female. They produce a daughter with Turner syndrome who is not color blind. What is the daughter's risk of developing hemophilia?.
8- A woman is affected with a mitochondrial disease. What proportion of her son's children will be affected with the disease? What proportion of her daughter's children will be affected with the disease?.
9- An autosomal dominant disorder is transmitted in each of these 3 pedigrees, and each pedigree member has been typed for a two-allele marker. Based on the genotypes in generation 3, what is the recombination rate between the disease locus and the marker locus?.
10- Continuing question 9, what is the LOD score for the hypothesis that r = 0 in these families?.
11- (essay) How has cloning and sequencing the cystic fibrosis gene led to a better understanding of causation, variable expression, and pleiotropy in this disorder?.
12- Questions 12-14 each present a pedigree. Match the pedigree with the most likely mode of inheritance. Note that complicating factors, such as reduced penetrance, may be present. Assume that the gene frequency of the disorder in the general population is very low. These answers may be used more than once?
13- Questions 12-14 each present a pedigree. Match the pedigree with the most likely mode of inheritance. Note that complicating factors, such as reduced penetrance, may be present. Assume that the gene frequency of the disorder in the general population is very low. These answers may be used more than once.?
14- Questions 12-14 each present a pedigree. Match the pedigree with the most likely mode of inheritance. Note that complicating factors, such as reduced penetrance, may be present. Assume that the gene frequency of the disorder in the general population is very low. These answers may be used more than once.?
15- Questions 15-17: Match each karyotype shown below with the appropriate description. The same answer can be used more than once. (Sorry that the images are not that clear)?
16- Questions 15-17: Match each karyotype shown below with the appropriate description. The same answer can be used more than once. (Sorry that the images are not that clear)?
17- Questions 15-17: Match each karyotype shown below with the appropriate description. The same answer can be used more than once. (Sorry that the images are not that clear)?
Powered by Issa Aldababseh